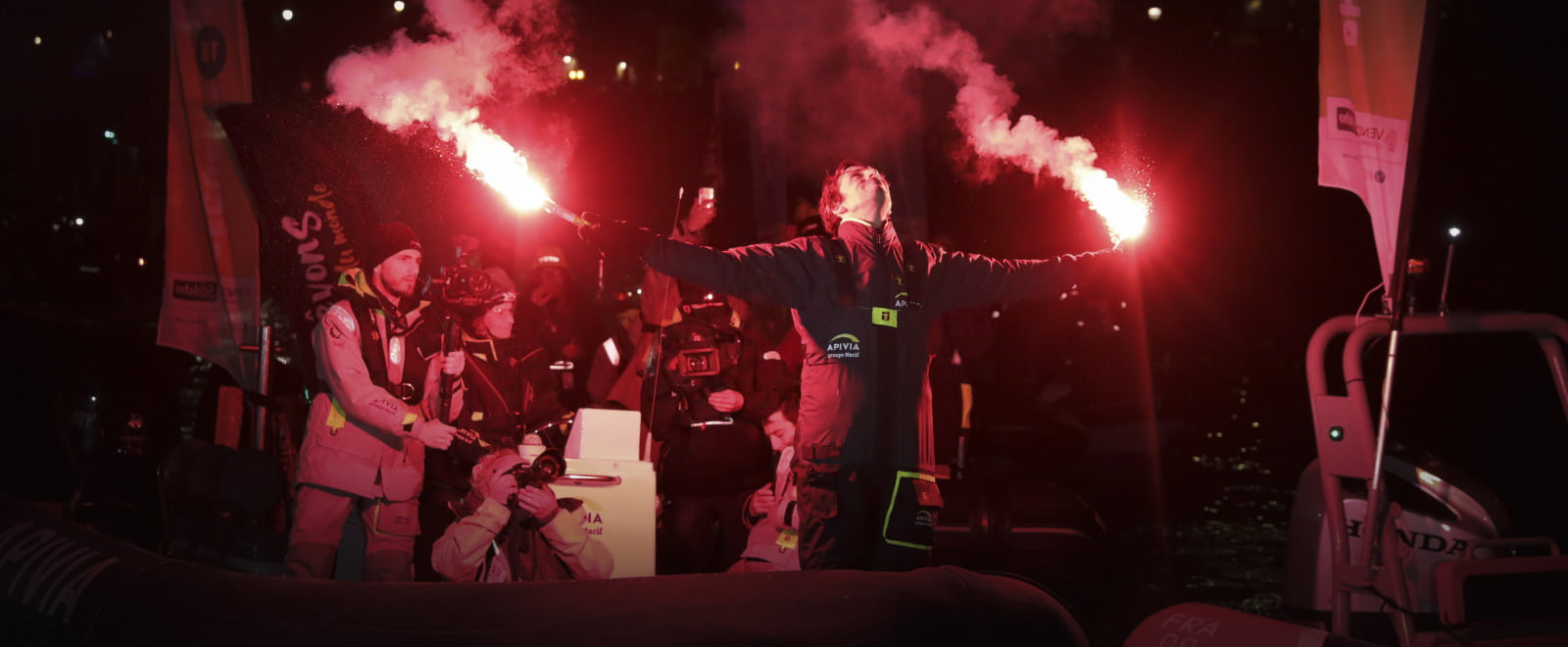
After an immaculately executed race, at 19h 35m 47s UTC this evening, after 80 days 6hrs 15mins 47secs since the start on Sunday 8th November, French skipper Charlie Dalin emerged from a damp, misty Bay of Biscay to break the finish line of the Vendée Globe, the solo, non-stop race round the world race, in first position and in doing so realised the ocean racing dreams of his youth.
But the 36-year-old skipper of APIVIA, who on Sunday November 8th started as one of the favourites to win this ninth edition of the Vendée Globe, now has to wait until two of his closest rivals have crossed the Les Sables d’Olonne finish line to see if victory is his.
Both Germany’s Boris Herrmann and French skipper Yannick Bestaven were allocated time allowances of six hours and ten hours and 15 minutes respectively for time and distance lost during their participation in the search for, and rescue of, stricken Kevin Escoffier whose IMOCA PRB effectively broke in two suddenly on November 30th, 550 miles SW of Cape Town, South Africa.
Although the win may end up going to one of the other two skippers – and the clock started when Dalin crossed the line – nothing can detract from Dalin’s immaculate, measured performance.
He has been the most regular and consistent leader throughout the 24,300 nautical mile race – which follows the traditional three capes route. His well prepared and optimised boat was launched early in the race quadrennial to maximise training miles. Dalin served notice he would be a serious contender when he won 2019’s Transat Jacques Vabre with Yann Eliès and finished second in July’s 3566 mile Vendée Arctic Les Sables race.
Dalin led at the Cape of Good Hope and Cape Leeuwin, and was a second to rival Bestaven at Cape Horn. That was despite damage to the bearing part of his port-side foil housing which meant his performance was compromised on starboard tack at least since he reported the problem on 14th December.
When he made a well-executed temporary repair, Dalin, who qualified as a naval architect in Southampton, England, kept himself in the race and still managed to offset the speed deficit he had on his closest challengers.
Slowed to a crawl for 18 hours he fulfilled a detailed repair plan developed in conjunction with his shore team who had sent accurate drawings of the replacement carbon composite chock he had to cut out and insert into the foil housing from the outside of the boat.
To complete the repair, he had to hang over the side of his boat on a halyard.
“I was going back and forwards between the cockpit and the foil exit location on the hull,” Dalin reported. “I was suspended by a halyard to reach the point where I could fit the chock and I don’t know how many times I went back and forth – 30 or 40 times – to adjust the carbon piece to fit the foil case.”
After rounding Cape Horn in second 15 hours behind the leader, on the tactical climb back up the South Atlantic he led the chasing peloton to recover more than 400 miles on runaway leader Bestaven who was snared in a light winds zone just south-east of Rio de Janeiro.
Although Dalin is a first timer on the Vendée Globe, like Bestaven and Herrmann among others – and indeed new to racing in the hostile southern oceans – his outstanding asset was sheer consistency, sailing carefully assessed, low risk strategies, smooth courses and manging himself and his IMOCA well.
Dalin’s Race
Aboard his latest generation Verdier designed boat, he briefly took the lead in the race on 11th November to the NE of the Azores. Limiting the risk to himself and his boat so early in the race, he chose to stay west and round tropical storm Thêta, the detour costing him around a hundred miles. It took him several days to regain the ground he lost, as he continued on his way down through the North Atlantic.
But when he crossed the Equator, he was already in the leading trio behind Britain’s Alex Thomson’s Hugo Boss and France’s Thomas Ruyant on LinkedOut. The trade winds in the Southern Hemisphere enabled him to express the full power of his foiler with several days of high-speed sailing, including notably on the 20th November, when he covered almost 507 miles. When they rounded the St. Helena high, Alex Thomson was forced to stop to carry out repairs and Dalin took the lead.
He led the fleet at high speed across the Southern Ocean when he topped the rankings for 22 days. He was the first to pass the Cape of Good Hope and Cape Leeuwin followed by Thomas Ruyant, Louis Burton and then Yannick Bestaven.
An outstanding sailor of his generation who has been on the Solitaire du Figaro podium four times and won the last Transat Jacques Vabre, he fought hard to defend his position, going as far as to hide his technical problem to avoid giving any advantage to his rivals. The damage to the port foil box was only revealed on 14th December, although he had clearly slowed down from 10th after coming out of severe gales shortly before Cape Leeuwin.
On starboard tack, Apivia was slower and was finally overtaken on 15th December by the two chasing boats, LinkedOut and Maître Coq. Dalin clung on to his place in the leading trio during the Pacific crossing. He was the second skipper to pass Cape Horn and played it brilliantly in the strategic battle as they climbed back up the South Atlantic regaining more than 400 miles from Yannick Bestaven to take the lead again on 12th January off Brazil.
The position of leader would then swing between him and Louis Burton. In the climb back up the North Atlantic in the trade winds and rounding the Azores high, which was positioned a long way south, Charlie remained much further east than Louis and went on to lead almost continuously to the finish line.
Charlie Dalin, the sailor
Although not from a sailing family, Dalin grew up in Le Havre, enchanted by the top skippers and their racing machines which mustered in the Channel port every two years for the two-handed coffee route transatlantic race from Le Havre to Brazil. His early racing career progressed along a traditional pathway, learning resourcefulness and self-reliance in the Mini650 class – in which he finished second in the 2007 MiniTransat – before he marked himself out as one of the outstanding talents of his generation in the Figaro offshore one design class, finishing four times on the La Solitaire du Figaro podium, third in 2014 and 2017 and second in 2015 and 2016.
Dalin shone initially in dinghy classes at the Le Havre club, recalling the formative thrill of sailing a double handed 420 dinghy on his own from the trapeze wire.
A natural perfectionist who sets himself very high standards and the possessor of a fast processing, numerate mind, Dalin graduated from the Skipper MACIF talent programme which backed him on the Figaro circuit, before being selected as skipper of a new Guillaume Verdier designed IMOCA.
He follows perfectly in the wake of François Gabart who won the 2012-13 Vendée Globe race in the MACIF Groupe’s colours and whose company MerConcept now manages the APIVIA IMOCA project.
America’s Cup winning designer Guillaume Verdier, who designed Dalin’s boat, remarks: “Charlie is just a superb strategist. He measures break even points well to evaluate the risk he is willing to take. And that is also what we tried to do when designing the boat.”
CHARLIE DALIN / APIVIA Statistics
Dalin raced the theoretical course of 24,365 nautical miles course at an average speed of 12.65kts
He actually sailed 28,268 miles at a race average of 14.67kts
The great passages
Equator (outwards)
Third place on 11/18/2020 at 21:03 UTC after 10d 07h 43min of racing
Cape of Good Hope
1st on 11/30/2020 11:11 UTC after 22d 09h 51min of racing
Cape Leeuwin
1st on 12/13/2020 11:25 UTC after 34d 22h 05min of racing
Cape Horn
2nd on 03/01/2021 04:39 UTC after 55d 15h 19min, 14hrs 56mins after leader Yannick Bestaven
Equator (back)
2nd on 01/16/2021 20:11 UTC after 69d 06h 51min, 59 minutes behind Louis Burton
Number of top rankings (Vendée Globe official rankings): 200
APIVIA November 11 21:00 UTC to November 12 04:00 UTC so 07:00 00:00
APIVIA November 23 08:00 UTC to December 15 04:00 UTC so 21d 20h 00min 00s
APIVIA December 25 08h00 UTC to December 26 04h00 UTC so 20h 00min 00s
APIVIA January 11 21:00 UTC to January 13 04:00 UTC so 1d 07h 00min 00s
APIVIA January 13 11:00 UTC to January 16 17:00 UTC so 3d 06h 00min 00s
APIVIA January 16 21:00 UTC to January 24 08:00 UTC so 7d 11h 00min 00s
APIVIA January 25 04h00 UTC to January 27 11h00 UTC so 2d 07h 00min 00s